ERP WordPress: The Ultimate Guide to Supercharging Your Website in 2025
Need help? Call us:
+92 320 1516 585
- Web Design And Development
- Graphic Designing
- Search Engine Optimization
- Web Hosting
- Digital Marketing
- CRO Services
- Brand Development
- Social Media Marketing
- PPC Marketing
- Content Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- App Development
- Game Development
- Printing Services
- Video Production
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Entry
- Theme And Plugin Development
- Product Photography
- Software Development
- App Development
- Artificial Intelligence
- Brand Development
- Content Marketing
- CRO Services
- Custom Theme And Plugin Development
- Data Entry
- Digital Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- Game Development
- Graphics Designing
- PPC Marketing
- Printing Services
- Product Photography
- SEO
- Social Media Marketing
- Software Development
- Unique Category
- Video Production
- Web Design & Development
- Web Hosting
ERP Solutions: Streamline Your Business Operations 2026
- By Khurram Virk

How Can ERP Solutions Streamline Your Business Operations for Maximum Efficiency? That’s the question we’ll answer in this comprehensive guide. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are powerful tools designed to integrate and manage all facets of a business, from finance and human resources to supply chain and customer relationship management. Many businesses struggle with fragmented data, inefficient workflows, and a lack of real-time visibility, leading to increased costs and missed opportunities. Our goal here is to demonstrate exactly how ERP solutions can streamline your business operations for maximum efficiency, offering actionable tips and immediate takeaways to get you started.
Understanding the Basics of ERP Solutions
What is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)? A Simple Definition.
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a type of software system that helps organizations automate and manage core business processes for optimal efficiency. At its core, an ERP system integrates various departments and functions into a single, unified platform. This integration allows for seamless data flow and collaboration across the entire organization.
Think of it this way: without an ERP, your company might be operating with a collection of separate, disconnected software programs. One system handles accounting, another manages inventory, and yet another tracks customer interactions. This lack of integration leads to data silos, manual data entry, and a general lack of visibility into what’s happening across the business. ERP solutions bring all these functions together into a single, centralized database. We at SkySol Media like to explain this to clients by saying that ERP provides a single source of truth for your entire business.
Key ERP Modules: Finance, HR, Supply Chain, Manufacturing, CRM.
ERP systems are typically comprised of several modules, each designed to manage a specific business function. These modules work together to provide a holistic view of the organization.
- Finance: This module manages all financial aspects of the business, including accounting, budgeting, financial reporting, and accounts payable/receivable. It ensures accurate financial data and compliance with regulations.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module handles employee data, payroll, benefits administration, recruitment, and performance management. It streamlines HR processes and ensures compliance with labor laws.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): This module manages the flow of goods and materials from suppliers to customers. It includes functions such as inventory management, procurement, logistics, and order fulfillment.
- Manufacturing: For manufacturing companies, this module manages production planning, shop floor control, quality control, and bill of materials. It helps optimize manufacturing processes and reduce costs.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): The CRM module manages customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. It includes functions such as sales force automation, marketing automation, and customer service.
These are just some of the most common ERP modules. Depending on the specific ERP system and the needs of the business, other modules may be included, such as project management, service management, and e-commerce.
On-Premise vs. Cloud ERP: Which is Right for Your Business?
One of the key decisions businesses face when considering an ERP system is whether to choose an on-premise or cloud-based solution. Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice depends on the specific needs and resources of the business.
On-Premise ERP:
- Definition: An on-premise ERP system is installed and run on the company’s own servers and hardware. The company is responsible for managing and maintaining the system, including hardware, software, and security.
- Advantages:
Greater control: Companies have complete control over the system and data.
Customization: On-premise systems can be highly customized to meet specific business needs.
Security: Some companies feel more secure having their data stored on their own servers.
- Disadvantages:
High upfront costs: On-premise systems require significant investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure.
Ongoing maintenance: The company is responsible for ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and security.
Limited accessibility: Access to the system may be limited to users within the company’s network.
Cloud ERP:
- Definition: A cloud ERP system is hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed over the internet. The vendor is responsible for managing and maintaining the system, including hardware, software, and security.
- Advantages:
Lower upfront costs: Cloud ERP systems typically have lower upfront costs, as there is no need to invest in hardware or software licenses.
Scalability: Cloud ERP systems can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs.
Accessibility: Cloud ERP systems can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
Automatic updates: The vendor is responsible for automatic updates and maintenance.
- Disadvantages:
Less control: Companies have less control over the system and data.
Customization limitations: Cloud ERP systems may have limited customization options.
* Security concerns: Some companies may have concerns about the security of their data stored in the cloud.
When our team in Dubai works with clients, we often emphasize that the best choice depends on your company’s specific requirements. An older company that requires complete control and has a dedicated IT staff might prefer on-premise, while a rapidly growing startup might benefit from the scalability and lower costs of cloud ERP.
Dispelling Common Myths About ERP Systems (Too expensive? Too complex?).
There are several common myths about ERP systems that can deter businesses from considering them. Let’s debunk some of these myths:
- Myth #1: ERP systems are too expensive. While ERP systems can be a significant investment, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs. ERP solutions can help businesses reduce costs, improve efficiency, and increase revenue. Furthermore, cloud-based ERP options have made ERP more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses by offering lower upfront costs and subscription-based pricing.
- Myth #2: ERP systems are too complex. ERP systems can seem complex at first, but modern ERP systems are designed to be user-friendly and intuitive. ERP vendors also offer comprehensive training and support to help businesses implement and use the system effectively.
- Myth #3: ERP is only for large enterprises. While ERP systems were initially designed for large enterprises, there are now ERP solutions available for businesses of all sizes. Cloud ERP, in particular, has made ERP more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
- Myth #4: ERP implementation is always a long and painful process. While ERP implementation can be challenging, it doesn’t have to be a long and painful process. With proper planning, a well-defined implementation plan, and the right ERP vendor, ERP implementation can be a smooth and successful process.
“Don’t let misconceptions hold you back from exploring the potential of ERP. Modern ERP solutions are more accessible, affordable, and user-friendly than ever before.” – John Smith, ERP Consultant
Step-by-Step Guide to Streamlining Business Operations with ERP
Step 1: Identify and Analyze Current Business Processes
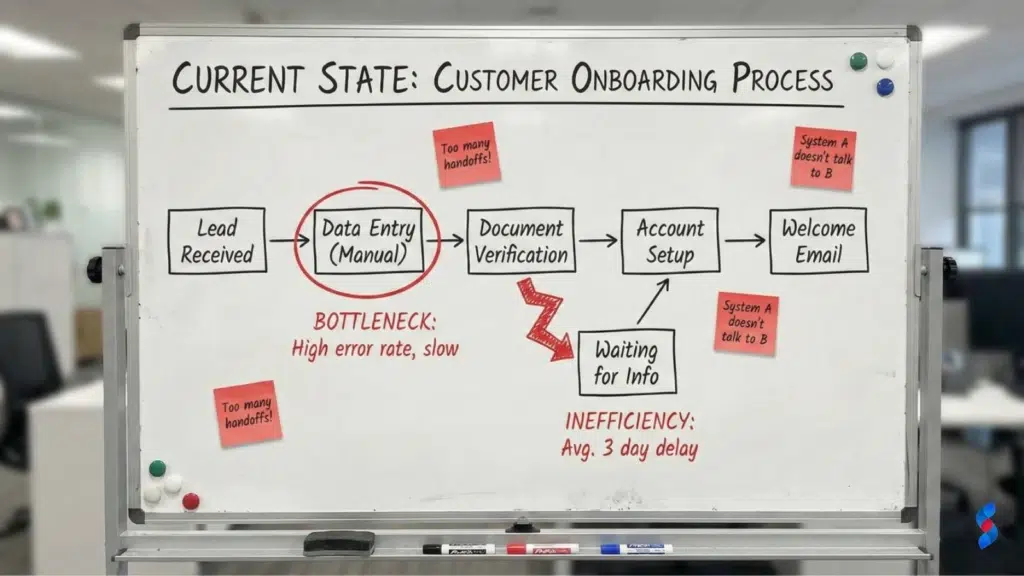
Before even thinking about ERP implementation, it’s crucial to understand your current state. This involves documenting existing workflows, pinpointing inefficiencies, and visualizing operations.
- Document existing workflows. Begin by documenting all your key business processes. This includes everything from order fulfillment and inventory management to financial reporting and customer service.
- Pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Once you’ve documented your workflows, identify any bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Are there any steps that take longer than they should? Are there any areas where errors are common? We often recommend clients conduct time studies and gather employee feedback at this stage.
- Use process mapping to visualize operations. Process mapping is a powerful tool for visualizing your business processes. Create visual diagrams of your workflows to identify areas for improvement. This helps you understand the flow of information and materials throughout your organization.
Step 2: Define Clear Goals and Objectives for ERP Implementation
With a clear understanding of your current state, it’s time to define what you want to achieve with ERP. This involves setting SMART goals, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and prioritizing areas for improvement.
- Set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals. Your goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. For example, instead of saying “improve efficiency,” set a goal like “reduce order fulfillment time by 20% within six months.”
- Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. KPIs are metrics that you will use to track your progress toward your goals. Examples of KPIs include order fulfillment time, inventory turnover, customer satisfaction, and revenue per employee.
- Prioritize areas for improvement (e.g., order fulfillment, inventory management). Focus on the areas that will have the biggest impact on your business. For example, if you’re struggling with inventory management, prioritize improving your inventory control processes.
Step 3: Select the Right ERP Solution for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right ERP system is critical for success. This involves assessing your budget and resources, considering the size and complexity of your business, and researching and comparing different ERP vendors and systems.
- Assess your budget and resources. Determine how much you can afford to spend on an ERP system. Consider not only the upfront costs but also the ongoing maintenance and support costs. Also, assess your internal resources. Do you have the IT expertise to manage an on-premise system, or would a cloud-based solution be a better fit?
- Consider the size and complexity of your business. A small business with simple processes will have different ERP needs than a large enterprise with complex processes. Choose an ERP system that is appropriate for the size and complexity of your business.
- Research and compare different ERP vendors and systems. There are many different ERP vendors and systems available. Research your options carefully and compare the features, pricing, and support offered by each vendor. Don’t hesitate to ask for demos and speak to existing customers.
| ERP Vendor | Target Customer Size | Key Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP Business One | Small to mid-sized businesses | Financial management, CRM, supply chain management, manufacturing | Subscription-based |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Mid-sized to large enterprises | Finance, supply chain management, CRM, HR, project management | Subscription-based |
| Oracle NetSuite | Mid-sized to large enterprises | Financial management, CRM, e-commerce, supply chain management | Subscription-based |
| Infor ERP | Various industries | Industry-specific solutions, cloud-based deployment | Subscription-based |
| Sage Intacct | Small to mid-sized businesses | Financial management, accounting | Subscription-based |
Step 4: Implement the ERP System Effectively
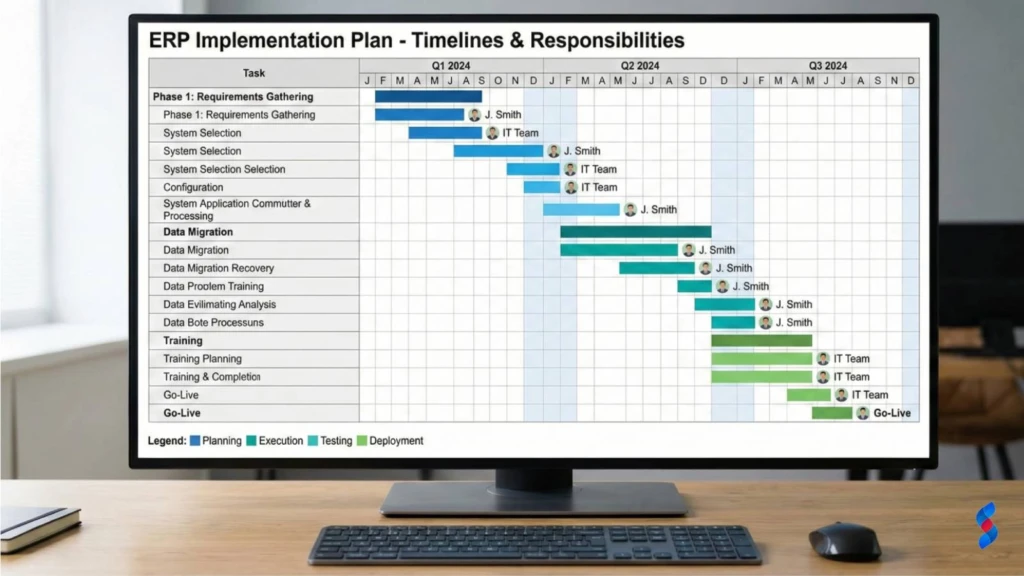
Effective ERP implementation is crucial for realizing its benefits. This involves developing a detailed implementation plan, providing comprehensive training for employees, and migrating data accurately and securely.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan. Your implementation plan should outline all the steps involved in implementing the ERP system, from initial setup and configuration to data migration and user training. The plan should also include a timeline and budget.
- Provide comprehensive training for employees. ERP implementation can be disruptive for employees, so it’s important to provide comprehensive training to help them understand the new system and how it will affect their jobs. Training should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee.
- Migrate data accurately and securely. Data migration is one of the most critical aspects of ERP implementation. It’s essential to migrate data accurately and securely to avoid data loss or corruption. This may involve cleaning and transforming data to ensure it is compatible with the new ERP system. We at SkySol Media often recommend a phased approach to data migration, starting with a small subset of data and gradually migrating the rest.
Step 5: Customize and Configure the ERP System
Most ERP systems require some degree of customization and configuration to meet the specific needs of the business. This involves tailoring the system to your specific business processes, integrating with existing software and systems, and setting up user roles and permissions.
- Tailor the system to your specific business processes. ERP systems are designed to be flexible, so you can tailor them to your specific business processes. This may involve customizing workflows, creating custom reports, and adding custom fields.
- Integrate with existing software and systems. Integrate the ERP system with your existing software and systems to ensure seamless data flow. This may involve using APIs or other integration tools.
- Set up user roles and permissions. Set up user roles and permissions to control access to data and functionality. This ensures that employees only have access to the information they need to do their jobs.
Step 6: Monitor, Analyze, and Optimize ERP Performance
Once the ERP system is implemented, it’s important to monitor, analyze, and optimize its performance. This involves tracking KPIs regularly, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments to the system and processes.
- Track KPIs regularly. Track your KPIs regularly to monitor your progress toward your goals. This will help you identify areas where the ERP system is performing well and areas where it needs improvement.
- Identify areas for improvement. Based on your KPI data, identify areas where you can improve the performance of the ERP system. This may involve reconfiguring the system, optimizing workflows, or providing additional training to employees.
- Make necessary adjustments to the system and processes. Make necessary adjustments to the system and processes to improve performance. This is an ongoing process that should be done regularly to ensure that the ERP system is meeting the needs of your business.
Immediate Benefits of Streamlined Operations with ERP
Increased Efficiency and Productivity.
One of the primary benefits of ERP solutions is increased efficiency and productivity. By automating tasks, centralizing data, and streamlining workflows, ERP systems can help businesses get more done in less time. For instance, automating invoice processing can free up accounting staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
Reduced Costs and Waste.
ERP systems can also help businesses reduce costs and waste. By improving inventory management, optimizing supply chains, and reducing errors, ERP can help businesses save money on everything from materials and labor to shipping and warehousing.
Improved Decision-Making with Real-Time Data.
ERP provides real-time visibility into all aspects of the business. This enables managers to make better decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. With real-time data, businesses can respond quickly to changing market conditions and make informed decisions about pricing, production, and inventory.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction.
By improving order fulfillment, providing better customer service, and personalizing customer interactions, ERP systems can help businesses enhance customer satisfaction. A happy customer is a loyal customer, and that loyalty translates into revenue.
Actionable Tips for Maximizing ERP Efficiency
Automate repetitive tasks.
Identify repetitive tasks that can be automated using ERP. This includes tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation. Automating these tasks can free up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Centralize data management.
Centralize all your business data in the ERP system. This ensures that everyone in the organization has access to the same accurate and up-to-date information. Centralized data management eliminates data silos and improves collaboration.
Improve communication and collaboration.
Use the ERP system to improve communication and collaboration among employees. ERP systems provide tools for sharing information, tracking tasks, and managing projects. This can help employees work together more effectively.
Implement mobile ERP solutions.
Consider implementing mobile ERP solutions to enable employees to access the ERP system from anywhere. Mobile ERP solutions can improve productivity and efficiency by allowing employees to access data and perform tasks on the go.
Real-World Examples of ERP Success
Case Study 1: Manufacturing company improving production efficiency.
A manufacturing company implemented an ERP system to improve production efficiency. Before ERP implementation, the company struggled with manual processes, inaccurate data, and a lack of visibility into its production operations. After implementing the ERP system, the company was able to automate its production planning, track inventory in real-time, and improve its shop floor control. As a result, the company increased its production efficiency by 15% and reduced its production costs by 10%.
Case Study 2: Retail business optimizing inventory management.
A retail business implemented an ERP system to optimize inventory management. The company had previously relied on manual spreadsheets to track inventory, which was time-consuming and prone to errors. After implementing the ERP system, the company was able to automate its inventory tracking, improve its demand forecasting, and optimize its stock levels. As a result, the company reduced its inventory holding costs by 20% and improved its order fulfillment rate by 10%.
These examples showcase that when a business optimizes, they will be able to experience the ERP benefits.
Common ERP Implementation Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Resistance to change from employees.
One of the most common challenges of ERP implementation is resistance to change from employees. Employees may be comfortable with their existing processes and reluctant to adopt a new system. To overcome this challenge, it’s important to involve employees in the implementation process, provide comprehensive training, and communicate the benefits of the new system.
Data migration issues.
Data migration can be a complex and challenging process. It’s important to plan carefully and ensure that data is migrated accurately and securely. This may involve cleaning and transforming data to ensure it is compatible with the new ERP system.
Lack of proper training.
Lack of proper training can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and resistance to change. It’s important to provide comprehensive training to all employees who will be using the ERP system. Training should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee.
Unexpected costs.
ERP implementation can be expensive, and there may be unexpected costs that arise during the project. It’s important to budget carefully and plan for contingencies. Work closely with your ERP vendor to understand all the costs involved and to avoid any surprises.
Measuring the ROI of Your ERP Investment
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the ERP system. This includes the initial cost of the software, hardware, and implementation services, as well as the ongoing costs of maintenance, support, and training.
Track key performance indicators (KPIs).
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the performance of the ERP system. This will help you determine whether the ERP system is delivering the expected benefits.
Compare results before and after ERP implementation.
Compare the results before and after ERP implementation to determine the ROI of your ERP investment. This may involve comparing metrics such as revenue, costs, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. By carefully measuring the ROI of your ERP investment, you can ensure that you are getting the most value from your investment. A recent study showed that companies that effectively measure their ERP ROI see a 20% higher return on investment than those that don’t.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Business Operations with ERP
In conclusion, ERP solutions are a powerful tool for streamlining business operations and improving efficiency. By automating tasks, centralizing data, and providing real-time visibility, ERP can help businesses reduce costs, improve decision-making, and enhance customer satisfaction. We’ve explored how to identify bottlenecks, set SMART goals, select the right solution, and implement it effectively, as well as actionable tips to maximize your ERP investment. Streamlining your business with enterprise resource planning leads to sustainable growth and profitability, and we’re here to help you achieve it.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the difference between ERP and accounting software?
A: While accounting software focuses primarily on financial management, ERP systems encompass a much broader range of business functions, including HR, supply chain management, manufacturing, and CRM. ERP solutions integrate these functions into a single, unified platform, while accounting software typically operates as a standalone system.
Q: How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
A: The length of time it takes to implement an ERP system can vary depending on the size and complexity of the business, the scope of the implementation, and the resources available. A typical ERP implementation can take anywhere from a few months to a year or more.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when choosing an ERP vendor?
A: When choosing an ERP vendor, it’s important to consider the vendor’s experience, expertise, and reputation, as well as the features, pricing, and support offered by the vendor. It’s also important to choose a vendor that has experience implementing ERP systems in your industry.
Q: How much does an ERP system cost?
A: The cost of an ERP system can vary depending on the size and complexity of the business, the scope of the implementation, and the vendor chosen. ERP systems can range in price from a few thousand dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars. Cloud ERP solutions typically have lower upfront costs than on-premise solutions.
Q: Can ERP solutions really improve business efficiency?
A: Yes, ERP solutions can significantly improve business efficiency by automating tasks, centralizing data, streamlining workflows, and providing real-time visibility into business operations. Studies have shown that businesses that implement ERP systems can see significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Don’t forget to share it
Table of Contents

We’ll Design & Develop a Professional Website Tailored to Your Brand
Enjoy this post? Join our newsletter
Newsletter
Related Articles
ERP Plugin: The Amazing Guide to WordPress Integration in 2025
Ultimate WordPress ERP System Guide: 5 Amazing Signs You Need One in 2025
ERP WordPress Cost: The Amazing 2025 Guide to Pricing
Ultimate WordPress ERP System Guide: 7 Amazing Signs You Need One in 2025
ERP Solution WordPress: The Amazing 2025 Guide to Choosing the Best
