On-Page SEO: The Amazing 2025 Checklist You’re Missing
Need help? Call us:
+92 320 1516 585
- Web Design And Development
- Graphic Designing
- Search Engine Optimization
- Web Hosting
- Digital Marketing
- CRO Services
- Brand Development
- Social Media Marketing
- PPC Marketing
- Content Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- App Development
- Game Development
- Printing Services
- Video Production
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Entry
- Theme And Plugin Development
- Product Photography
- Software Development
- App Development
- Artificial Intelligence
- Brand Development
- Content Marketing
- CRO Services
- Custom Theme And Plugin Development
- Data Entry
- Digital Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- Game Development
- Graphics Designing
- PPC Marketing
- Printing Services
- Product Photography
- SEO
- Social Media Marketing
- Software Development
- Unique Category
- Video Production
- Web Design & Development
- Web Hosting
On-Page SEO: Avoid Mistakes & Boost Traffic 2026
- By Khurram Virk

On-Page SEO is the foundation of a successful online presence. It’s about optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. When done right, On-Page SEO can significantly boost your organic traffic, improve user experience, and increase conversions. However, many businesses unknowingly commit common mistakes that hinder their On-Page SEO efforts, preventing them from achieving their desired results. This article will guide you through these pitfalls and provide actionable solutions to avoid them, ensuring your website reaches its full potential.
Mistake #1: Ignoring Keyword Research
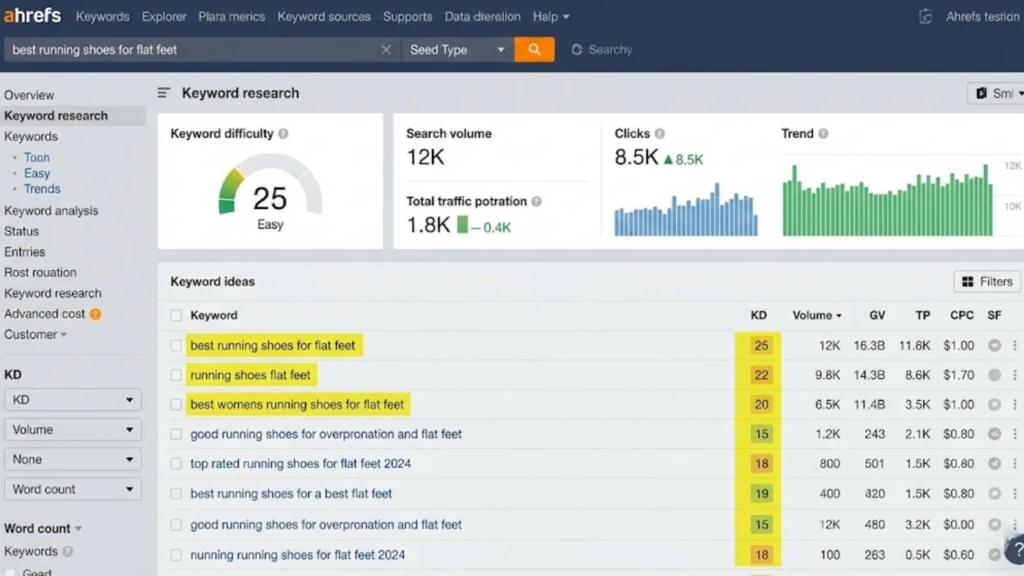
One of the most fundamental errors in On-Page SEO is neglecting keyword research. Without understanding what your target audience is searching for, you’re essentially shooting in the dark. We’ve seen countless clients who initially targeted keywords that, while relevant to their business, had virtually no search volume, resulting in minimal organic traffic.
Targeting Keywords with Low Search Volume
Focusing on keywords with extremely low search volume is like opening a store in a deserted town. Even if your store is perfect, there simply aren’t enough people around to generate substantial business. Choosing keywords with a monthly search volume of zero or very few searches can be a waste of time and resources.
Neglecting Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that people use when they’re closer to making a purchase or seeking a specific answer. Ignoring these keywords means missing out on highly qualified traffic. When our team in Dubai analyzes client data, they often find that long-tail keywords, while individually generating less traffic, collectively contribute a significant portion of overall organic traffic and conversions.
Solution: Utilize Keyword Research Tools
Leverage powerful keyword research tools such as Semrush, Ahrefs, and Google Keyword Planner to identify relevant keywords. These tools provide valuable data on search volume, keyword difficulty, and related keyword suggestions, helping you make informed decisions. These tools help you understand the landscape and find opportunities others might miss.
Solution: Identify Relevant Keywords with Decent Search Volume and Low Competition
Focus on keywords that strike a balance between search volume and competition. Targeting keywords with high search volume but also high competition can be challenging, especially for new websites. Look for “sweet spot” keywords that have a decent search volume and relatively lower competition. This allows you to rank more easily and start generating traffic sooner. We recommend aiming for keywords with a keyword difficulty score below 40 on tools like Ahrefs or Semrush for initial targets.
Solution: Incorporate Long-Tail Keywords to Capture Niche Traffic
Integrate long-tail keywords into your content strategy. Create blog posts, articles, and landing pages that specifically address these longer, more specific search queries. For example, instead of just targeting “coffee maker,” target “best coffee maker for small apartments under $100.” This strategy can attract highly targeted traffic and improve your conversion rates.
“Keyword research is the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. Without it, you’re essentially guessing. Focus on understanding your audience’s search behavior and identifying keywords that align with their needs and your business goals.” – Neil Patel
Mistake #2: Neglecting Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are crucial elements of On-Page SEO. They are the first impression your website makes on potential visitors in search engine results pages (SERPs). Neglecting these elements can significantly impact your click-through rates (CTR) and ultimately, your organic traffic.
Using Generic or Duplicate Title Tags
Using generic title tags like “Home” or “About Us” provides no valuable information to search engines or users. Duplicate title tags across multiple pages can also confuse search engines and dilute your ranking potential. We once had a client whose website had the same title tag on every single page. Once we updated those to be unique and descriptive, we saw a 20% increase in organic traffic within the first month.
Writing Uncompelling or Missing Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are short summaries of your page content that appear below the title tag in SERPs. Missing or poorly written meta descriptions can deter users from clicking on your link. A bland or uninformative meta description is a missed opportunity to entice potential visitors.
Exceeding Character Limits
Search engines typically display only a limited number of characters in title tags and meta descriptions. Exceeding these limits can result in truncated text, making your listings look unprofessional and less appealing. As of 2026, Google typically displays the first 50-60 characters of a title tag and the first 150-160 characters of a meta description.
Solution: Craft Unique and Keyword-Rich Title Tags for Each Page (Under 60 Characters)
Create unique and descriptive title tags for each page on your website. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally and keep them under 60 characters to ensure they are fully displayed in SERPs. The title tag should accurately reflect the content of the page and entice users to click. For example, instead of “Blog Post,” use “On-Page SEO Tips: Avoid Mistakes & Boost Traffic in 2026.”
Solution: Write Compelling Meta Descriptions That Accurately Summarize the Page Content (Under 160 Characters)
Write compelling meta descriptions that accurately summarize the content of each page. Highlight the key benefits and value proposition to entice users to click. Keep them under 160 characters to avoid truncation. Think of your meta description as a mini-advertisement for your page.
Solution: Include a Clear Call to Action in the Meta Description
Incorporate a clear call to action (CTA) in your meta description. Encourage users to take the next step, such as “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Download Now.” A strong CTA can significantly improve your CTR and drive more traffic to your website. This is a simple yet powerful technique to improve results.

Mistake #3: Improper Use of Header Tags (H1-H6)
Header tags (H1-H6) are used to structure content and provide visual hierarchy. They also play a crucial role in SEO by signaling to search engines the important topics and subtopics on a page. Incorrectly using header tags can negatively impact both readability and search engine rankings.
Using Multiple H1 Tags on a Single Page
The H1 tag should be used for the main title of the page and should only be used once. Using multiple H1 tags can confuse search engines and dilute the importance of your main topic. Think of the H1 tag as the headline of a newspaper article – there should only be one.
Skipping Header Tag Levels (e.g., H1 to H3 Directly)
Header tags should be used in a logical and hierarchical order. Skipping levels (e.g., going from H1 to H3 without an H2) can disrupt the flow of your content and make it difficult for search engines to understand the structure of your page.
Not Using Keywords in Header Tags
Header tags provide an excellent opportunity to incorporate relevant keywords and signal to search engines the main topics of your content. Neglecting to use keywords in header tags is a missed optimization opportunity.
Solution: Use Only One H1 Tag per Page, Typically for the Main Title
Ensure that each page on your website has only one H1 tag, and that it accurately reflects the main title of the page. This helps search engines understand the primary topic of your content. The H1 tag should be the most prominent heading on the page and should be visually distinct from other header tags.
Solution: Use Header Tags (H2-H6) to Structure Content Logically and Hierarchically
Use header tags (H2-H6) to structure your content logically and hierarchically. Break down your content into smaller, more manageable sections and use header tags to introduce each section. This makes your content easier to read and understand for both users and search engines.
Solution: Incorporate Relevant Keywords Naturally into Header Tags
Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into your header tags. Use keywords that accurately reflect the content of each section and help search engines understand the topics being discussed. Avoid keyword stuffing, which can negatively impact your rankings. We aim for a natural inclusion of keywords, ensuring they fit seamlessly within the context.
[IMAGE: Example of a webpage with properly structured header tags (H1, H2, H3) showing a clear content hierarchy.]
Mistake #4: Poor Quality & Thin Content
Content is the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. Low-quality or thin content fails to engage users, satisfy search engines, and ultimately, achieve your desired results. Creating valuable, in-depth, and original content is essential for attracting and retaining organic traffic.
Writing Short, Uninformative Articles (“Thin Content”)
Thin content refers to articles or pages that are short, lack substance, and provide little value to the user. These pages often fail to address user intent and are unlikely to rank well in search engines. A page with only a few sentences and no real information is essentially invisible to search engines.
Plagiarizing Content from Other Websites
Plagiarism is a serious offense that can result in severe penalties from search engines. Copying content from other websites not only violates copyright laws but also damages your reputation and credibility. Search engines prioritize original content and penalize websites that engage in plagiarism.
Lack of Proper Formatting and Readability
Poorly formatted content that is difficult to read can frustrate users and increase bounce rates. Walls of text, inconsistent formatting, and a lack of visual aids can make it challenging for users to find the information they need. Users are more likely to leave a website if the content is not visually appealing and easy to consume.
Solution: Create In-Depth, Valuable, and Original Content That Addresses User Intent
Focus on creating in-depth, valuable, and original content that addresses user intent. Conduct thorough research to understand what your target audience is searching for and create content that provides comprehensive answers to their questions. Aim to provide unique insights, perspectives, and value that differentiate your content from the competition.
Solution: Ensure Content is Well-Written, Properly Formatted, and Easy to Read
Ensure that your content is well-written, properly formatted, and easy to read. Use clear and concise language, avoid jargon, and proofread your content carefully for errors. Proper formatting includes using headings, subheadings, bullet points, and white space to break up the text and make it more visually appealing.
Solution: Use Headings, Subheadings, Bullet Points, and Visuals to Enhance Readability
Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and visuals (images, videos, infographics) to enhance readability and make your content more engaging. These elements help break up the text, highlight key points, and make it easier for users to scan and find the information they need. Visuals can also help illustrate complex concepts and make your content more memorable.
[IMAGE: Example of a well-formatted blog post with headings, subheadings, bullet points, images, and white space to enhance readability.]
Mistake #5: Ignoring Internal Linking
Internal linking is the practice of linking to other relevant pages within your own website. It’s a crucial aspect of On-Page SEO that helps improve site navigation, distribute link equity, and signal to search engines the importance of different pages. Failing to link internally can hinder your website’s SEO performance.
Not Linking to Relevant Pages within the Website
Failing to link to relevant pages within your website can make it difficult for users and search engines to discover your content. Internal links act as pathways that guide users and search engines to other valuable resources on your website.
Using Generic Anchor Text (e.g., “click here”)
Anchor text is the clickable text used in a link. Using generic anchor text like “click here” or “read more” provides no valuable information to search engines about the content being linked to. Descriptive anchor text is essential for signaling the relevance of the linked page.
Over-Linking or Under-Linking
Both over-linking and under-linking can be detrimental to your website’s SEO. Over-linking can make your content look spammy and dilute the value of each link. Under-linking can result in isolated pages that are difficult to discover.
Solution: Link to Relevant Pages within Your Website Using Descriptive Anchor Text
Link to relevant pages within your website using descriptive anchor text that accurately reflects the content of the linked page. For example, instead of “click here,” use “learn more about on-page SEO strategies.” This helps search engines understand the context of the link and the topic of the linked page.
Solution: Create a Logical Internal Linking Structure to Guide Users and Search Engines
Create a logical internal linking structure that guides users and search engines through your website. Link to relevant pages within your content to provide additional information and resources. This helps users navigate your website more easily and encourages them to explore more of your content.
Solution: Prioritize Linking to High-Value or Cornerstone Content
Prioritize linking to high-value or cornerstone content – the most important and comprehensive pages on your website. These pages should be the focus of your internal linking efforts, as they often represent the core topics and services you offer. This helps boost their authority and ranking potential.
| Internal Linking Best Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Relevance | Link to pages that are directly related to the current content. |
| Anchor Text | Use descriptive and keyword-rich anchor text. |
| Placement | Place links naturally within the content, where they provide the most value to the reader. |
| Quantity | Link strategically, avoiding both over-linking and under-linking. |
| Hierarchy | Prioritize linking to high-value and cornerstone content. |
[IMAGE: Example of a blog post with strategic internal links to relevant pages within the website.]
Mistake #6: Overlooking Image Optimization
Images play a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal and user experience of your website. However, unoptimized images can slow down page load speed and miss SEO opportunities. Optimizing your images is essential for improving both user experience and search engine rankings.
Using Large, Uncompressed Image Files
Large, uncompressed image files can significantly slow down your website’s loading speed. This can lead to a poor user experience and negatively impact your search engine rankings. Optimizing your images for the web is crucial for improving site speed.
Not Using Descriptive Alt Text for Images
Alt text (alternative text) is a short description of an image that is displayed when the image cannot be loaded or when a user is using a screen reader. Not using descriptive alt text for images is a missed SEO opportunity. Alt text helps search engines understand the content of your images and their relevance to the page.
Neglecting Image File Names
Image file names also provide an opportunity to incorporate relevant keywords and signal to search engines the content of your images. Neglecting to use descriptive file names is a missed optimization opportunity.
Solution: Compress Images to Reduce File Size Without Sacrificing Quality
Compress your images to reduce file size without sacrificing quality. Use image optimization tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel to reduce the file size of your images while maintaining their visual quality. This can significantly improve your website’s loading speed.
Solution: Use Descriptive Alt Text for All Images, Incorporating Relevant Keywords
Use descriptive alt text for all images on your website. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into the alt text to help search engines understand the content of your images and their relevance to the page. The alt text should accurately describe the image and provide context for users who cannot see the image.
Solution: Use Descriptive File Names for Images (e.g., on-page-seo-guide.jpg)
Use descriptive file names for your images. Instead of using generic file names like “IMG_1234.jpg,” use descriptive file names that incorporate relevant keywords, such as “on-page-seo-guide.jpg” or “best-keyword-research-tools.jpg.” This helps search engines understand the content of your images and their relevance to the page.
[IMAGE: Screenshot of an image optimization tool showing the compression of an image file.]
Mistake #7: Neglecting Mobile-Friendliness
In today’s mobile-first world, having a mobile-friendly website is no longer optional – it’s essential. A non-mobile-friendly website alienates mobile users and hurts your SEO. Ensuring your website is optimized for mobile devices is crucial for attracting and retaining organic traffic.
Website Not Being Responsive
A responsive website adapts to different screen sizes and devices, providing an optimal viewing experience for users on desktops, tablets, and smartphones. A non-responsive website can be difficult to navigate and use on mobile devices, leading to a poor user experience.
Using Unreadable Font Sizes on Mobile Devices
Using font sizes that are too small to read on mobile devices can frustrate users and make it difficult for them to consume your content. Ensuring that your font sizes are readable on mobile devices is crucial for providing a positive user experience.
Slow Loading Times on Mobile
Slow loading times on mobile devices can lead to high bounce rates and lower rankings. Mobile users are often on the go and have less patience for slow-loading websites. Optimizing your website for fast loading times on mobile devices is crucial for retaining mobile users and improving your SEO.
Solution: Ensure Your Website is Responsive and Adapts to Different Screen Sizes
Ensure that your website is responsive and adapts to different screen sizes. Use a responsive design framework or theme that automatically adjusts the layout and content of your website to fit different screen sizes. Test your website on different devices to ensure it provides an optimal viewing experience for all users.
Solution: Use Readable Font Sizes and Mobile-Friendly Navigation
Use readable font sizes and mobile-friendly navigation on your website. Ensure that your font sizes are large enough to read easily on mobile devices and that your navigation is easy to use with touch gestures. Use a mobile-friendly menu that is easy to access and navigate.
Solution: Optimize Your Website for Fast Loading Times on Mobile Devices
Optimize your website for fast loading times on mobile devices. Compress images, leverage browser caching, minimize HTTP requests, and use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to improve loading times on mobile devices. Test your website’s loading speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and identify areas for improvement.
[IMAGE: Screenshot of a website displayed on different devices (desktop, tablet, smartphone) showing its responsiveness.]
Mistake #8: Ignoring URL Structure
Your website’s URL structure plays a crucial role in both user experience and SEO. Poor URL structures can confuse users and search engines, while well-structured URLs can improve your website’s visibility and ranking potential.
Using Long, Complex URLs with Unnecessary Parameters
Long, complex URLs with unnecessary parameters can be difficult to read and understand for both users and search engines. These URLs often look messy and unprofessional, which can deter users from clicking on them.
Not Using Keywords in URLs
URLs provide an opportunity to incorporate relevant keywords and signal to search engines the topic of the page. Not using keywords in URLs is a missed SEO opportunity.
Inconsistent URL Structure Across the Website
Inconsistent URL structures across the website can confuse users and search engines, making it difficult to understand the organization of your website. A consistent URL structure is essential for maintaining a clean and user-friendly website.
Solution: Create Short, Descriptive URLs That Include Relevant Keywords
Create short, descriptive URLs that include relevant keywords. Use keywords that accurately reflect the content of the page and help search engines understand the topic being discussed. Avoid using unnecessary parameters and keep your URLs as concise as possible. For example, instead of using a URL like /page?id=1234, use /on-page-seo-guide.
Solution: Use a Consistent URL Structure Across Your Website
Use a consistent URL structure across your website. Choose a URL structure that is logical and easy to understand for both users and search engines. For example, you might use a structure like /category/subcategory/page-title for blog posts or /products/product-name for product pages.
Solution: Avoid Using Unnecessary Parameters in URLs
Avoid using unnecessary parameters in URLs. Parameters can make your URLs longer and more complex, which can negatively impact user experience and SEO. If possible, use static URLs instead of dynamic URLs with parameters.
[IMAGE: Examples of good and bad URL structures, highlighting the benefits of short, descriptive URLs with keywords.]
Mistake #9: Slow Page Load Speed
Page load speed is a critical ranking factor that affects both user experience and SEO. Slow loading times lead to high bounce rates and lower rankings, while fast loading times improve user engagement and search engine visibility.
Large Image Files
Large image files are one of the most common causes of slow page load speeds. Optimizing your images for the web is crucial for improving site speed and user experience.
Excessive HTTP Requests
Excessive HTTP requests can also slow down your website’s loading speed. Each time a user visits your website, their browser sends requests to the server for each file (images, CSS, JavaScript) needed to display the page. Reducing the number of HTTP requests can significantly improve loading times.
Poorly Optimized Code
Poorly optimized code can also contribute to slow page load speeds. Clean, efficient code loads faster and improves the overall performance of your website.
Solution: Optimize Images, Leverage Browser Caching, and Minimize HTTP Requests
Optimize images by compressing them, using appropriate file formats (e.g., WebP), and resizing them to the correct dimensions. Leverage browser caching to store static assets (images, CSS, JavaScript) in the user’s browser, reducing the need to download them on subsequent visits. Minimize HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files, using CSS sprites, and reducing the number of external resources.
Solution: Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to Distribute Content Globally
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute your website’s content across multiple servers around the world. This allows users to download content from the server closest to them, reducing latency and improving loading times.
Solution: Optimize Your Website’s Code to Improve Loading Times
Optimize your website’s code by minifying CSS and JavaScript files, removing unnecessary code, and using efficient coding practices. This can significantly improve your website’s loading speed and overall performance.
[IMAGE: Screenshot of Google PageSpeed Insights showing a website’s performance score and recommendations for improvement.]
Mistake #10: Not Monitoring & Analyzing Results
On-Page SEO is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and analysis. Failing to track and analyze your On-Page SEO efforts prevents you from identifying areas for improvement and optimizing your website for better results.
Not Using Google Analytics or Google Search Console
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are essential tools for tracking and analyzing your website’s performance. Not using these tools means missing out on valuable data that can help you improve your On-Page SEO.
Not Tracking Keyword Rankings or Organic Traffic
Tracking keyword rankings and organic traffic is crucial for measuring the effectiveness of your On-Page SEO efforts. Not tracking these metrics makes it difficult to determine whether your efforts are paying off and to identify areas where you need to make adjustments.
Not Analyzing User Behavior on the Website
Analyzing user behavior on your website (e.g., bounce rate, time on page, conversion rate) can provide valuable insights into how users are interacting with your content and where you can make improvements. Not analyzing user behavior means missing out on opportunities to optimize your website for better user experience and conversions.
Solution: Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to Track Your Website’s Performance
Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track your website’s performance. These tools provide valuable data on traffic, keyword rankings, user behavior, and other key metrics. Set up goals and track conversions to measure the effectiveness of your On-Page SEO efforts.
Solution: Monitor Keyword Rankings, Organic Traffic, Bounce Rate, and Other Key Metrics
Monitor keyword rankings, organic traffic, bounce rate, and other key metrics regularly. Track your progress over time and identify trends and patterns that can help you optimize your website for better results. Use this data to make informed decisions about your On-Page SEO strategy.
Solution: Analyze User Behavior to Identify Areas for Improvement
Analyze user behavior on your website to identify areas for improvement. Use heatmaps, session recordings, and other tools to understand how users are interacting with your content and where they are encountering problems. Use this information to optimize your website for better user experience and conversions.
[IMAGE: Screenshot of Google Analytics dashboard showing key metrics such as organic traffic, bounce rate, and conversion rate.]
Conclusion: Mastering On-Page SEO for Organic Growth
We’ve covered ten critical On-Page SEO mistakes that can hinder your website’s performance and prevent you from achieving your desired results. Remember to avoid neglecting keyword research, title tags and meta descriptions, header tags, content quality, internal linking, image optimization, mobile-friendliness, URL structure, page load speed, and monitoring/analysis.
Effective On-Page SEO requires continuous monitoring and optimization. By consistently implementing the strategies discussed in this article, you can improve your website’s search engine rankings, attract more organic traffic, and achieve your business goals.
We, at SkySol Media, are here to help you navigate the complexities of On-Page SEO. We believe that by implementing these strategies, you can see a real change in your website’s overall performance.
FAQ Section
Q: How often should I update my On-Page SEO?
A: On-Page SEO is an ongoing process. You should regularly review and update your On-Page SEO elements (title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, content, etc.) to ensure they are optimized for relevant keywords and user intent. We recommend reviewing your On-Page SEO at least quarterly.
Q: What is the ideal length for a blog post?
A: The ideal length for a blog post depends on the topic and the level of detail required to address user intent. However, generally, longer, more in-depth articles tend to perform better in search engines. We recommend aiming for at least 1500-2000 words for comprehensive blog posts.
Q: How important is mobile-friendliness for SEO in 2026?
A: Mobile-friendliness is extremely important for SEO in 2026. Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it primarily uses the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking. If your website is not mobile-friendly, it will likely suffer in search engine rankings.
Q: What are some free tools for keyword research?
A: Some free tools for keyword research include Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, and Ubersuggest. These tools provide valuable data on search volume, keyword suggestions, and related keywords. While paid tools often offer more advanced features, these free tools can be a good starting point for keyword research.
Q: How can I improve my website’s page load speed?
A: You can improve your website’s page load speed by optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, minimizing HTTP requests, using a Content Delivery Network (CDN), and optimizing your website’s code. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help you identify areas for improvement.
Don’t forget to share it
Table of Contents

We’ll Design & Develop a Professional Website Tailored to Your Brand
Enjoy this post? Join our newsletter
Newsletter
Related Articles
On-page SEO: The Ultimate Checklist for an Amazing 2025 Website
On-Page SEO: The Ultimate Checklist Missing These Amazing Elements in 2025
On-Page SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Amazing Rankings in 2025
On-Page SEO: 5 Amazing Fixes to Rank #1 in 2025
Ultimate On-Page SEO Audit: Is Your Website Invisible? (2025)
