UX Conversions: Ultimate Guide to Boosting Conversions in 2025
Need help? Call us:
+92 320 1516 585
- Web Design And Development
- Graphic Designing
- Search Engine Optimization
- Web Hosting
- Digital Marketing
- CRO Services
- Brand Development
- Social Media Marketing
- PPC Marketing
- Content Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- App Development
- Game Development
- Printing Services
- Video Production
- Artificial Intelligence
- Data Entry
- Theme And Plugin Development
- Product Photography
- Software Development
- App Development
- Artificial Intelligence
- Brand Development
- Content Marketing
- CRO Services
- Custom Theme And Plugin Development
- Data Entry
- Digital Marketing
- ERP Solutions
- Game Development
- Graphics Designing
- PPC Marketing
- Printing Services
- Product Photography
- SEO
- Social Media Marketing
- Software Development
- Unique Category
- Video Production
- Web Design & Development
- Web Hosting
UI UX: The Amazing Guide to Stop Losing Customers in 2026
- By Khurram Virk

In today’s competitive digital landscape, UI UX design is more critical than ever for businesses looking to retain customers and drive conversions. A well-designed UI UX can significantly enhance user satisfaction, increase engagement, and ultimately, improve your bottom line. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essential aspects of UI UX, providing actionable insights to help you stop losing customers in 2026 and beyond.
Understanding the Impact of UI/UX on Customer Retention
What is UI/UX and Why Does It Matter?
UI UX, or User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX), encompasses the entire journey a user takes when interacting with your product or service. UI focuses on the visual elements and interactive components that users directly engage with, while UX encompasses the overall feeling and satisfaction a user derives from that interaction. A strong UI UX is crucial because it directly impacts customer perception, usability, and ultimately, customer retention.
Defining User Interface (UI)
The user interface (UI) is the point of interaction between a user and a digital device or product. It includes all the visual elements, such as buttons, icons, typography, color schemes, and layout, that enable users to interact with a system. A well-designed user interface is visually appealing, intuitive, and easy to navigate. It enhances the overall user experience by making it simple and enjoyable for users to accomplish their goals. Good UI design adheres to UI design principles, ensuring consistency, clarity, and efficiency. The UI is also what the user will think of as the website design itself.
Defining User Experience (UX)
User experience (UX) encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a company, its services, and its products. UX design aims to create a seamless, intuitive, and satisfying experience for users, from the initial discovery of a product to its ongoing use. It involves understanding user needs, behaviors, and motivations through research and testing. Effective UX design considers factors such as usability, accessibility, desirability, and value. The goal of UX is to ensure that every interaction a user has with a product is positive and contributes to a long-lasting, loyal relationship. In essence, UX design seeks to answer the question, “What is the customer thinking and feeling?”
The Direct Correlation Between UI/UX and Customer Retention
The direct correlation between UI UX and customer retention is undeniable. A positive user experience fosters loyalty, while a negative one can lead to frustration and churn. When users find a website or app easy to use, visually appealing, and helpful, they are more likely to return and recommend it to others. Conversely, if they encounter confusing navigation, slow loading times, or frustrating interactions, they are likely to abandon the product and seek alternatives. Therefore, investing in UI UX improvements is a strategic move to enhance customer satisfaction and boost retention rates. The better the user experience, the better the rate of customer retention.
Statistics on How Poor UI/UX Affects Conversions
Poor UI UX can have a devastating impact on conversions. Consider these statistics:
- Nearly 90% of online consumers are less likely to return to a site after a poor experience.
- A negative mobile experience makes 80% of users less likely to purchase from that company again.
- Every $1 invested in UX results in a return of $100 (a 9,900% ROI).
These figures highlight the critical importance of prioritizing UI UX to avoid losing potential customers and revenue. Addressing usability issues and improving overall design can lead to significant gains in conversions and customer loyalty.
Case Studies of Companies That Improved Customer Retention Through UI/UX Improvements
Numerous companies have successfully improved customer retention by focusing on UI UX improvements.
Example 1: Airbnb
Airbnb revamped its UI UX to provide a more personalized and intuitive experience. They focused on improving search functionality, enhancing the visual presentation of listings, and streamlining the booking process. As a result, they saw a significant increase in user engagement and customer retention.
Example 2: Dropbox
Dropbox simplified its user interface and improved the onboarding process for new users. They also introduced features that made it easier for users to collaborate and share files. These changes led to a substantial increase in customer satisfaction and a decrease in churn.
Example 3: Amazon
Amazon continuously invests in UI UX to optimize the shopping experience. They focus on personalized recommendations, seamless checkout processes, and providing clear and helpful product information. These efforts have contributed to their high customer retention rates and dominance in the e-commerce market.
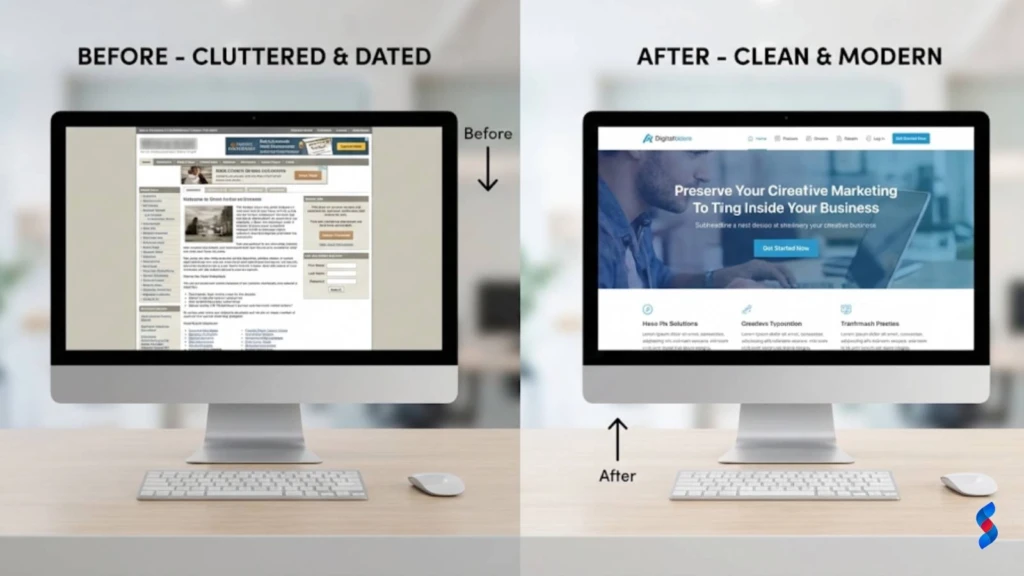
Identifying UI/UX Problems That Are Driving Customers Away
Conducting a UX Audit: A Step-by-Step Guide
A UX audit is a comprehensive evaluation of your website or app’s user experience. It helps identify areas where improvements can be made to enhance usability and customer satisfaction. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with the audit. Are you trying to increase conversions, reduce bounce rates, or improve customer satisfaction?
2. Gather Data: Collect data from various sources, including analytics tools, user surveys, and feedback forms.
3. Evaluate Usability: Assess the ease of use of your website or app. Are users able to easily find what they are looking for?
4. Analyze Accessibility: Ensure your website or app is accessible to users with disabilities.
5. Review Design: Evaluate the visual design of your website or app. Is it visually appealing and consistent with your brand?
6. Identify Issues: Compile a list of UI UX problems that are negatively impacting the user experience.
7. Prioritize Issues: Rank the issues based on their impact and the effort required to fix them.
8. Develop Recommendations: Create a detailed plan for addressing the identified issues.
9. Implement Changes: Implement the recommended changes and track their impact on key metrics.
10. Repeat: Regularly conduct UX audits to ensure continuous improvement.
Analyzing User Behavior with Analytics Tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Hotjar)
Analytics tools like Google Analytics and Hotjar provide valuable insights into user behavior on your website or app. By analyzing data such as page views, bounce rates, time on page, and conversion rates, you can identify areas where users are struggling or dropping off. Google Analytics is a must for any company doing website design.
- Google Analytics helps you understand where your users are coming from, what pages they are visiting, and how long they are staying on each page.
- Hotjar provides heatmaps, session recordings, and feedback polls to help you visualize user interactions and gather qualitative data.
By combining these tools, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how users are interacting with your product and identify opportunities for UI UX improvements.
Heatmaps and Scroll Maps: Visualizing User Interactions
Heatmaps and scroll maps are visual tools that help you understand how users interact with your website or app.
- Heatmaps show you where users are clicking, tapping, and moving their mouse, indicating areas of high and low engagement.
- Scroll maps show you how far users are scrolling down a page, revealing whether they are seeing important content.
By analyzing these visual representations of user behavior, you can identify areas where users are getting stuck or missing key information. This data can then be used to optimize your UI UX and improve engagement.
User Surveys and Feedback Forms: Gathering Qualitative Data
User surveys and feedback forms are valuable tools for gathering qualitative data about user experiences. By asking users directly about their thoughts, feelings, and frustrations, you can gain a deeper understanding of their needs and expectations.
- User surveys can be used to gather feedback on specific aspects of your website or app, such as usability, design, or content.
- Feedback forms can be placed on key pages to allow users to provide real-time feedback on their experience.
Analyzing the responses from these surveys and forms can help you identify UI UX problems that are not apparent from quantitative data alone.
Common UI/UX Mistakes That Lead to Customer Frustration
Several common UI UX mistakes can lead to customer frustration and churn. Avoiding these mistakes is crucial for creating a positive user experience.
- Poor Navigation: Confusing or inconsistent navigation can make it difficult for users to find what they are looking for.
- Slow Loading Times: Slow loading times can lead to frustration and abandonment.
- Lack of Mobile Responsiveness: Websites that are not optimized for mobile devices provide a poor experience for mobile users.
- Complex Forms: Long and complex forms can deter users from completing them.
- Inconsistent Design: Inconsistent design can make a website or app feel unprofessional and untrustworthy.
- Lack of Accessibility: Websites that are not accessible to users with disabilities exclude a significant portion of the population.
Slow Loading Times and Performance Issues
Slow loading times and performance issues are major drivers of customer frustration. Users expect websites and apps to load quickly and respond instantly to their actions. When a website or app is slow or unresponsive, users are likely to abandon it and seek alternatives.
- Optimize Images: Compress images to reduce their file size without sacrificing quality.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Enable browser caching to store frequently accessed resources locally.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of HTTP requests by combining files and using CSS sprites.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute your content across multiple servers to reduce latency.
- Optimize Code: Optimize your code to improve performance and reduce loading times.
Confusing Navigation and Information Architecture
Confusing navigation and information architecture can make it difficult for users to find what they are looking for. When users are unable to easily navigate a website or app, they are likely to become frustrated and leave.
- Use Clear and Concise Labels: Use labels that accurately describe the content of each page or section.
- Create a Logical Hierarchy: Organize your content in a logical hierarchy that makes sense to users.
- Provide Breadcrumbs: Use breadcrumbs to help users understand their location within the website or app.
- Implement a Search Function: Provide a search function to allow users to quickly find specific content.
- Test Your Navigation: Test your navigation with real users to ensure it is intuitive and easy to use.
Lack of Mobile Responsiveness
In today’s mobile-first world, a lack of mobile responsiveness is a major UI UX mistake. Websites that are not optimized for mobile devices provide a poor experience for mobile users, leading to frustration and abandonment.
- Use Responsive Design: Use responsive design to ensure your website adapts to different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Optimize for Touch Gestures: Optimize your website for touch gestures, such as swiping and pinching.
- Use Mobile-Friendly Navigation: Use a mobile-friendly navigation menu that is easy to use on small screens.
- Optimize Images for Mobile: Optimize images for mobile devices to reduce loading times.
- Test on Multiple Devices: Test your website on a variety of mobile devices to ensure it works properly.
Accessibility Issues for Users with Disabilities
Accessibility is a critical aspect of UI UX design. Websites that are not accessible to users with disabilities exclude a significant portion of the population and may be in violation of accessibility laws.
- Provide Alternative Text for Images: Provide alternative text for images to allow screen readers to describe them to visually impaired users.
- Use Sufficient Color Contrast: Use sufficient color contrast to ensure that text is readable for users with low vision.
- Make Your Website Keyboard-Accessible: Ensure that all interactive elements can be accessed using a keyboard.
- Use ARIA Attributes: Use ARIA attributes to provide additional information to assistive technologies.
- Test with Accessibility Tools: Test your website with accessibility tools to identify and fix accessibility issues.
The Power of User-Centered Design
What is User-Centered Design (UCD)?
User-centered design (UCD) is an iterative design process in which the needs, wants, and limitations of end users are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. UCD aims to create highly usability and accessible products for the user.
The Core Principles of UCD
The core principles of UCD include:
- Focus on Users: Understand your users’ needs, goals, and motivations.
- Empathy: Put yourself in your users’ shoes and see the world from their perspective.
- Iteration: Continuously test and refine your design based on user feedback.
- Collaboration: Involve users and stakeholders in the design process.
- Accessibility: Design for users of all abilities.
By adhering to these principles, you can create products that are truly user-friendly and effective.
Empathy: Understanding Your Users’ Needs and Goals
Empathy is a critical component of UCD. By understanding your users’ needs, goals, and motivations, you can design products that truly meet their needs.
- Conduct User Research: Conduct user interviews, surveys, and observations to gather insights into user behavior.
- Create User Personas: Develop user personas to represent your target audience.
- Use Empathy Maps: Create empathy maps to visualize your users’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Iteration: Testing and Refining Your Design
Iteration is a key principle of UCD. By continuously testing and refining your design based on user feedback, you can ensure that your product is truly user-friendly and effective.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Test your design with real users to identify areas for improvement.
- Gather Feedback: Collect feedback from users through surveys, feedback forms, and social media.
- Analyze Data: Analyze user data to identify patterns and trends.
- Implement Changes: Implement changes based on user feedback and data analysis.
How to Implement UCD in Your Design Process
Implementing UCD in your design process involves incorporating user feedback at every stage.
1. Research: Conduct user research to understand your target audience.
2. Design: Create initial designs based on your research findings.
3. Test: Test your designs with real users.
4. Analyze: Analyze user feedback and data.
5. Iterate: Refine your designs based on your analysis.
6. Repeat: Repeat the process until you have a product that meets your users’ needs.
Creating User Personas: Representing Your Target Audience
User personas are fictional representations of your target audience. They are based on research and data about your users and help you to understand their needs, goals, and motivations.
- Give Your Persona a Name and Photo: Make your persona feel real by giving them a name and photo.
- Describe Their Demographics: Include information about their age, gender, occupation, and location.
- Outline Their Goals and Motivations: Describe what they are trying to achieve and why.
- Identify Their Pain Points: Identify the challenges and frustrations they experience.
- Create a Scenario: Create a scenario that describes how they would use your product.
User Journey Mapping: Visualizing the User Experience
User journey mapping is a visual representation of the steps a user takes to achieve a specific goal. It helps you understand the user’s experience from their perspective and identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Define the Goal: Define the goal that the user is trying to achieve.
- Identify the Steps: Identify the steps the user takes to achieve the goal.
- Map the Emotions: Map the user’s emotions at each step.
- Identify Pain Points: Identify the pain points the user experiences at each step.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Brainstorm solutions to address the pain points.
Usability Testing: Getting Feedback From Real Users
Usability testing involves observing real users as they interact with your product. It helps you identify usability problems and areas where improvements can be made.
- Recruit Participants: Recruit participants who represent your target audience.
- Create Tasks: Create tasks that users will perform during the test.
- Observe Users: Observe users as they perform the tasks.
- Gather Feedback: Gather feedback from users after they complete the tasks.
- Analyze Results: Analyze the results to identify usability problems.
“The best way to predict the future is to design it.” – Buckminster Fuller
[IMAGE: A photo of a usability testing session, showing a user interacting with a website while being observed by a researcher.]
Optimizing Your UI for Maximum Conversions
Streamlining the User Flow for Key Actions
Streamlining the user flow for key actions is crucial for maximizing conversions. A clear and intuitive user flow makes it easy for users to complete their desired actions, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Identify Key Actions: Identify the key actions you want users to take.
- Map the User Flow: Map the steps users take to complete those actions.
- Eliminate Unnecessary Steps: Eliminate any unnecessary steps in the user flow.
- Simplify the Process: Simplify the process as much as possible.
- Test the Flow: Test the flow with real users to ensure it is intuitive.
Reducing the Number of Clicks to Complete a Task
Reducing the number of clicks to complete a task can significantly improve the user experience and increase conversions. The fewer clicks required, the less friction users experience, making them more likely to complete the task.
- Simplify Forms: Simplify forms by reducing the number of fields.
- Use Autocomplete: Use autocomplete to fill in information automatically.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Provide clear instructions to guide users through the process.
- Use One-Page Checkout: Use a one-page checkout process to streamline the checkout experience.
Clear and Concise Call-to-Actions (CTAs)
Clear and concise call-to-actions (CTAs) are essential for guiding users towards desired actions. A well-designed CTA should be visually prominent, easy to understand, and compelling.
- Use Action-Oriented Language: Use action-oriented language that tells users what to do.
- Make It Visually Prominent: Make the CTA visually prominent by using a contrasting color and a clear font.
- Place It Strategically: Place the CTA in a strategic location where users are likely to see it.
- Test Different CTAs: Test different CTAs to see which ones perform best.
Visual Hierarchy: Guiding Users’ Eyes to Important Elements
Visual hierarchy is the arrangement of elements on a page in a way that guides users’ eyes to the most important information. A well-designed visual hierarchy makes it easy for users to scan the page and quickly find what they are looking for.
- Use Size and Scale: Use size and scale to make important elements stand out.
- Use Color and Contrast: Use color and contrast to draw attention to key elements.
- Use Typography: Use typography to create a visual hierarchy and guide users’ eyes.
- Use White Space: Use white space to create separation between elements and improve readability.
Optimizing Form Design for Increased Completion Rates
Simple and Intuitive Form Fields
Optimizing form design is crucial for increasing completion rates. A well-designed form should be simple, intuitive, and easy to complete.
- Use Clear Labels: Use clear labels to explain what information is needed.
- Use Appropriate Input Fields: Use appropriate input fields for each type of information.
- Minimize the Number of Fields: Minimize the number of fields to reduce the amount of effort required.
- Group Related Fields: Group related fields together to make the form more organized.
Progress Indicators for Multi-Step Forms
Progress indicators are helpful for multi-step forms, as they give users a sense of how much progress they have made and how much is left to complete. This can help reduce frustration and increase completion rates.
- Use a Visual Progress Bar: Use a visual progress bar to show users their progress.
- Provide Clear Labels: Provide clear labels for each step in the form.
- Highlight the Current Step: Highlight the current step to make it clear to users where they are in the process.
Error Prevention and Helpful Error Messages
Error prevention and helpful error messages are essential for a positive user experience. By preventing errors from occurring in the first place and providing helpful error messages when they do occur, you can reduce frustration and increase completion rates.
- Use Input Masks: Use input masks to ensure that users enter data in the correct format.
- Provide Real-Time Validation: Provide real-time validation to check for errors as users type.
- Use Clear Error Messages: Use clear error messages that explain what went wrong and how to fix it.
- Place Error Messages Near the Input Field: Place error messages near the input field that caused the error.
Designing a UX That Keeps Customers Coming Back
Creating a Consistent Brand Experience Across All Touchpoints
Creating a consistent brand experience across all touchpoints is crucial for building brand loyalty and customer retention. When users encounter a consistent experience across your website, app, social media, and customer service interactions, they are more likely to develop a strong connection with your brand.
- Use Consistent Visuals: Use consistent visuals, such as logos, colors, and typography, across all touchpoints.
- Maintain a Consistent Tone of Voice: Maintain a consistent tone of voice in your messaging.
- Provide Consistent Customer Service: Provide consistent customer service across all channels.
- Ensure a Consistent User Experience: Ensure a consistent user experience across all platforms and devices.
Personalization: Tailoring the Experience to Individual Users
Personalization involves tailoring the user experience to individual users based on their preferences, behaviors, and demographics. By providing a personalized experience, you can increase user engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
- Use Personalized Recommendations: Use personalized recommendations to suggest products or content that users may be interested in.
- Tailor Content to User Preferences: Tailor content to user preferences based on their past behavior.
- Use Personalized Greetings: Use personalized greetings to welcome users back to your website or app.
- Provide Personalized Offers: Provide personalized offers based on user demographics and purchase history.
Anticipating User Needs and Providing Proactive Support
Anticipating user needs and providing proactive support can significantly enhance the user experience and increase customer loyalty. By anticipating potential problems and providing solutions before users even encounter them, you can demonstrate that you care about their experience.
- Provide Helpful Documentation: Provide helpful documentation and tutorials to guide users.
- Offer Proactive Support: Offer proactive support through chat, email, or phone.
- Use Predictive Analytics: Use predictive analytics to identify users who may need help.
- Provide Personalized Recommendations: Provide personalized recommendations for solutions.
Gamification: Adding Elements of Fun and Reward
Gamification involves adding elements of fun and reward to the user experience. By incorporating game-like elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, you can increase user engagement and motivation.
- Use Points and Badges: Use points and badges to reward users for completing tasks.
- Create Leaderboards: Create leaderboards to foster competition and motivation.
- Offer Rewards: Offer rewards for achieving milestones.
- Make It Fun: Make the experience fun and engaging.
Building a Community Around Your Product or Service
Building a community around your product or service can foster customer loyalty and advocacy. By creating a space where users can connect with each other, share their experiences, and provide feedback, you can build a strong and engaged community.
- Create a Forum or Online Community: Create a forum or online community where users can connect with each other.
- Host Events: Host events to bring users together in person.
- Encourage User-Generated Content: Encourage users to create and share content related to your product or service.
- Provide Support and Moderation: Provide support and moderation to ensure a positive community experience.
The Importance of Mobile-First Design
Why Mobile Optimization is Crucial in Today’s Market
Mobile optimization is crucial in today’s market because the majority of internet users access the web through mobile devices. A website that is not optimized for mobile provides a poor user experience and can lead to frustration and abandonment.
- Mobile Usage is Growing: Mobile usage is growing rapidly, while desktop usage is declining.
- Mobile-Friendly Sites Rank Higher: Google prioritizes mobile-friendly sites in search results.
- Mobile Users Expect a Seamless Experience: Mobile users expect a seamless and intuitive experience.
- Mobile Drives Conversions: Mobile devices are increasingly used for online purchases.
Designing for Different Screen Sizes and Resolutions
Designing for different screen sizes and resolutions is essential for providing a consistent user experience across all devices. A responsive design adapts to different screen sizes, ensuring that the website looks and functions properly on any device.
- Use a Responsive Framework: Use a responsive framework, such as Bootstrap or Foundation.
- Use Flexible Layouts: Use flexible layouts that adapt to different screen sizes.
- Use Scalable Images: Use scalable images that adjust to different resolutions.
- Test on Multiple Devices: Test your website on a variety of devices to ensure it works properly.
Implementing Responsive Design Principles
Implementing responsive design principles involves using flexible layouts, scalable images, and media queries to adapt your website to different screen sizes.
- Use Flexible Grids: Use flexible grids that adjust to different screen sizes.
- Use Scalable Images: Use scalable images that adjust to different resolutions.
- Use Media Queries: Use media queries to apply different styles based on screen size.
Optimizing for Touch Gestures and Mobile Navigation
Optimizing for touch gestures and mobile navigation is crucial for providing a positive user experience on mobile devices. Mobile users interact with websites using touch gestures, such as swiping and pinching, and require a mobile-friendly navigation menu.
- Use Touch-Friendly Buttons: Use touch-friendly buttons that are easy to tap.
- Use Swipe Gestures: Use swipe gestures to navigate between pages.
- Use a Mobile-Friendly Menu: Use a mobile-friendly menu that is easy to use on small screens.
Testing Your Mobile UI/UX on Various Devices
Testing your mobile UI UX on various devices is essential for ensuring that your website looks and functions properly on all devices.
- Use Emulators and Simulators: Use emulators and simulators to test your website on different devices.
- Test on Real Devices: Test your website on real devices to get an accurate representation of the user experience.
- Gather Feedback from Mobile Users: Gather feedback from mobile users to identify areas for improvement.
Accessibility: Designing for Everyone
Understanding Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Understanding Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is essential for designing websites that are accessible to users with disabilities. WCAG provides a set of guidelines for making web content more accessible to people with a wide range of disabilities, including visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, language, learning, and neurological disabilities.
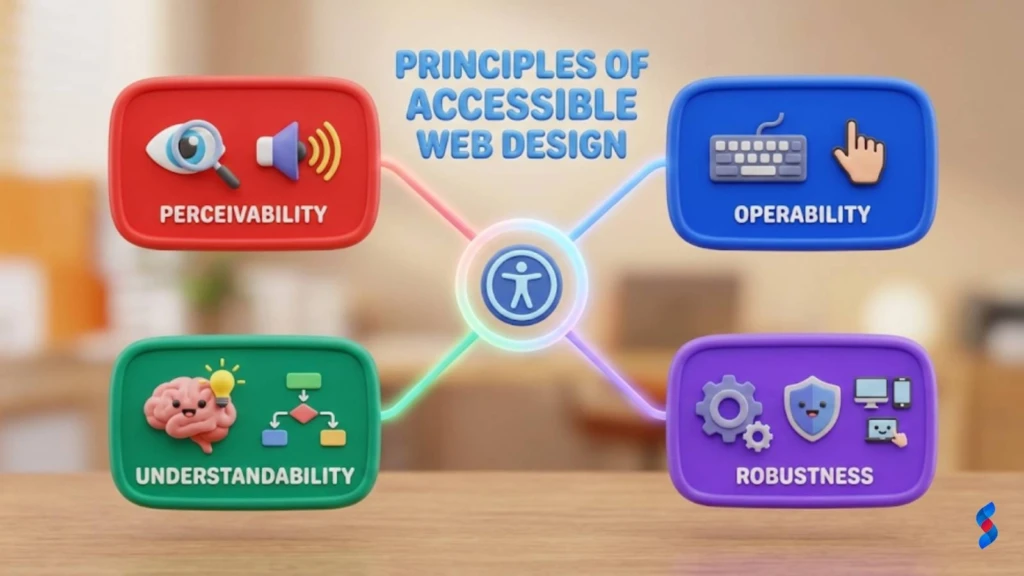
Ensuring Your Website is Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust
Ensuring your website is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust is the foundation of accessibility. These four principles guide the development of accessible web content.
- Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presentable to users in ways they can perceive.
- Operable: User interface components and navigation must be operable.
- Understandable: Information and the operation of the user interface must be understandable.
- Robust: Content must be robust enough that it can be interpreted reliably by a wide variety of user agents, including assistive technologies.
Providing Alternative Text for Images
Providing alternative text for images is crucial for making your website accessible to visually impaired users. Alternative text is a text description of an image that is read by screen readers, allowing visually impaired users to understand the content of the image.
- Use Descriptive Text: Use descriptive text that accurately describes the content of the image.
- Keep It Concise: Keep the alternative text concise and to the point.
- Avoid Redundant Text: Avoid redundant text that repeats information already provided in the surrounding text.
Using Sufficient Color Contrast
Using sufficient color contrast is essential for making your website accessible to users with low vision. Sufficient color contrast ensures that text is readable against the background color.
- Use a Contrast Checker: Use a contrast checker to ensure that your color combinations meet WCAG standards.
- Choose High-Contrast Colors: Choose high-contrast colors that are easy to read.
- Avoid Low-Contrast Combinations: Avoid low-contrast combinations that are difficult to read.
Making Your Website Keyboard-Accessible
Making your website keyboard-accessible is crucial for users who cannot use a mouse. Keyboard accessibility ensures that all interactive elements can be accessed and operated using a keyboard.
- Use Logical Tab Order: Use a logical tab order that follows the visual flow of the page.
- Provide Visual Focus Indicators: Provide visual focus indicators to show users which element is currently focused.
- Ensure All Elements are Keyboard-Accessible: Ensure that all interactive elements, such as buttons and links, are keyboard-accessible.
Testing Your Website with Accessibility Tools
Testing your website with accessibility tools is essential for identifying and fixing accessibility issues. Accessibility tools can help you identify problems such as missing alternative text, insufficient color contrast, and keyboard accessibility issues.
- Use Automated Testing Tools: Use automated testing tools, such as WAVE or Axe, to identify common accessibility issues.
- Use Screen Readers: Use screen readers, such as NVDA or VoiceOver, to test your website from the perspective of a visually impaired user.
- Conduct Manual Testing: Conduct manual testing to identify issues that may not be detected by automated tools.
| Accessibility Guideline | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Text for Images | Provide descriptive text for images so screen readers can convey the image’s content to visually impaired users. | <img src="example.jpg" alt="A smiling woman using a laptop"> |
| Color Contrast | Ensure sufficient color contrast between text and background for readability. | Use contrast checkers to verify a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 for normal text. |
| Keyboard Accessibility | Make all interactive elements navigable using a keyboard. | Ensure all buttons and links can be accessed via the ‘Tab’ key. |
| Form Labels | Associate labels with form fields so screen readers can announce the purpose of each field. | <label for="name">Name:</label><input type="text" id="name" name="name"> |
| ARIA Attributes | Use ARIA attributes to provide additional semantic information to assistive technologies. | <button aria-label="Close">X</button> |
[IMAGE: A person using a screen reader to navigate a website, highlighting the importance of accessible design.]
Measuring the Success of Your UI/UX Improvements
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of your UI UX improvements. By monitoring these metrics, you can determine whether your changes are having a positive impact on user engagement, satisfaction, and conversions.
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. An increase in conversion rate indicates that your UI UX improvements are making it easier for users to complete their desired actions.
Bounce Rate
Bounce rate is the percentage of users who leave your website after viewing only one page. A decrease in bounce rate indicates that your UI UX improvements are making your website more engaging and relevant to users.
Time on Page
Time on page is the amount of time users spend on a particular page. An increase in time on page indicates that your UI UX improvements are making your content more engaging and informative.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score
Customer satisfaction (CSAT) score is a measure of how satisfied customers are with their experience. A higher CSAT score indicates that your UI UX improvements are enhancing customer satisfaction.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a measure of customer loyalty and advocacy. It asks customers how likely they are to recommend your product or service to others. A higher NPS indicates that your UI UX improvements are fostering customer loyalty.
A/B Testing: Comparing Different Design Options
A/B testing involves comparing two different versions of a design to see which one performs better. By A/B testing different design options, you can identify the most effective UI UX improvements.
- Create Two Versions: Create two versions of the design that you want to test.
- Split Your Traffic: Split your traffic evenly between the two versions.
- Track Key Metrics: Track key metrics, such as conversion rate and bounce rate.
- Analyze Results: Analyze the results to determine which version performed better.
- Implement the Winning Version: Implement the winning version of the design.
Analyzing the Results and Making Data-Driven Decisions
Analyzing the results of your UI UX measurements and making data-driven decisions is crucial for continuous improvement. By analyzing your data, you can identify patterns and trends that can inform your design decisions.
- Use Analytics Tools: Use analytics tools, such as Google Analytics and Hotjar, to track key metrics.
- Create Reports: Create reports to summarize your findings.
- Share Your Findings: Share your findings with your team and stakeholders.
- Develop Action Plans: Develop action plans to address any issues that are identified.
Common Misconceptions About UI/UX
Myth #1: UI and UX are the Same Thing
One of the most common misconceptions is that UI and UX are the same thing. While they are related and work together, they are distinct disciplines. UI focuses on the visual design and interactive elements of a product, while UX encompasses the overall experience a user has with the product.
Myth #2: UI/UX is Only Important for Websites
Another common myth is that UI UX is only important for websites. In reality, UI UX is important for any product or service that involves user interaction, including apps, software, hardware, and even physical products.
Myth #3: Good UI/UX is Expensive
Some people believe that good UI UX is expensive. While it is true that investing in UI UX requires resources, the return on investment can be significant. Good UI UX can lead to increased conversions, customer satisfaction, and loyalty, ultimately boosting your bottom line.
Myth #4: Once UI/UX is Done, It Doesn’t Need to Be Updated
A final misconception is that once UI UX is done, it doesn’t need to be updated. In reality, UI UX is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, testing, and refinement. User needs and expectations change over time, so it is important to regularly update your UI UX to stay relevant and competitive.
The Future of UI/UX Design
Emerging Trends in UI/UX
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of UI UX design.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in UX
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing an increasingly important role in UX design. AI and ML can be used to personalize the user experience, anticipate user needs, and provide proactive support.
Voice User Interface (VUI) and Conversational Design
Voice user interface (VUI) and conversational design are becoming more popular as voice assistants, such as Siri and Alexa, become more prevalent. VUI allows users to interact with products and services using their voice, while conversational design focuses on creating natural and intuitive voice interactions.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are creating new opportunities for UI UX design. VR and AR allow users to interact with digital content in a more immersive and engaging way.
The Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The field of UI UX design is constantly evolving, so it is important to embrace continuous learning and adaptation. Staying up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices is crucial for remaining competitive and delivering exceptional user experiences.
UI/UX Tools and Resources
Top UI Design Software (e.g., Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch)
Several UI design software options are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most
Don’t forget to share it
Table of Contents

We’ll Design & Develop a Professional Website Tailored to Your Brand
Enjoy this post? Join our newsletter
Newsletter
Related Articles
UI UX Design: The Ultimate Guide to a Winning Strategy in 2025
Accessible UX Design: 5 Amazing Ways to Ensure Inclusivity in 2025
Ultimate Guide: UX Writing – Enhance Your UI Design in 2025
UI/UX Conversions: Proven Ways to Boost Sales in 2025
UX Design Conversions: The Ultimate Guide to Amazing Growth in 2025
